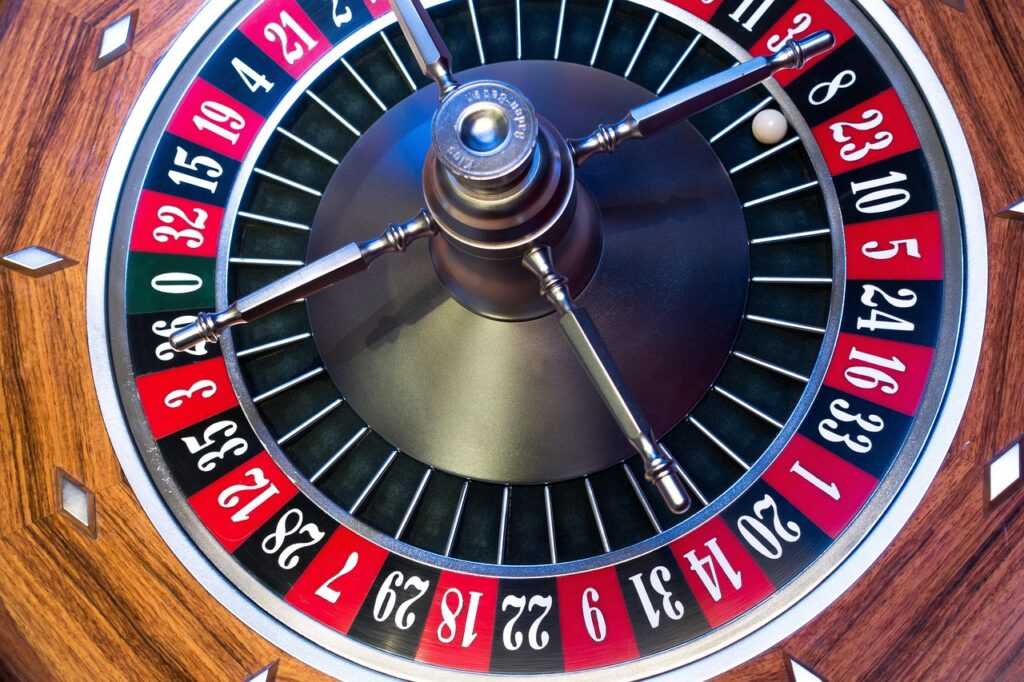
Understanding Near Misses
Near misses, events where success is just out of reach, strongly impact our emotions and behaviors. Research by psychologists shows that near misses often heighten motivation and performance. When people come close to a goal, like just missing a winning lottery ticket, they experience a mix of emotional arousal and frustration. This unique combination sparks a desire to try again, aiming harder for success.
Most commonly seen in gambling, sports, and goal-oriented activities, near misses exploit our brains’ reward systems. In gambling, getting two out of three matching symbols can feel almost rewarding, pushing individuals to play more. Studies indicate that these near wins activate the same brain regions as actual wins, illustrating why these moments feel exciting and promising.
In sports, athletes often use near misses as motivators. Missing a game-winning shot by inches can push players to train harder, correcting minor errors to ensure a better outcome next time. Similarly, near misses in academic or professional goals, such as narrowly missing a promotion or just missing high grades, can drive individuals to achieve higher standards of work and excellence.
Understanding this phenomenon isn’t just academic; it has practical implications for personal growth and development. Recognizing that almost winning can be powerful provides insights into resilience and the motivation to push forward in various life aspects. Near misses demonstrate how close encounters with success can shape behavior and drive future performance more effectively.
Psychological Impact of Near Misses
Near misses profoundly influence our psychology. By narrowly missing success, we experience distinct emotional and cognitive reactions that can significantly affect future behaviors and decisions.
Dopamine Response
Near misses trigger a dopamine response in the brain. Dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward, spikes in levels when individuals perceive they almost won. This biological reaction heightens arousal and motivation, making future attempts more appealing. Research shows that even in the absence of a tangible reward, the brain’s reward system remains active, encouraging continued effort. For instance, gamblers often continue playing after near misses because the dopamine release creates an enticing illusion of imminent success.
Motivational Boost
- The motivational boost from near misses is well-documented.
- When individuals fall just short of their goals, the frustration felt acts as a powerful catalyst for effort.
- Near misses create a psychological state where the potential for winning feels within reach, filling people with determination to try again.
- Athletes, for example, often channel the energy from near misses into more rigorous training and practice, aiming to surpass previous performances.
- Similarly, in professional settings, narrowly missing a promotion can spark an increased focus on skill improvement and job performance.
Case Studies and Examples
Research shows that near misses can significantly impact behavior and motivation. Here are some real-world examples.
Gambling Scenarios
In gambling, near misses are common and influential. Slot machines often show two out of three winning symbols, creating a near-win experience. Studies by Reid (1986) indicate that these near wins increase gamblers’ arousal and urge to play again. Casinos design games to capitalize on this psychological response, leading individuals to invest more money and time, hoping for an actual win. Near misses make players believe they are close to winning, fueling their gambling addiction.
Sports and Competitions

Athletes and competitors frequently encounter near misses. In sports, losing by a narrow margin, like a missed goal or a close race, stimulates athletes’ drive to improve. A study by Abaci and Oz (2019) found that near misses in athletic performance lead to increased motivation and subsequent effort in training. For example, an Olympian missing a medal by milliseconds often uses the experience to fuel their training regimen, aiming for perfection in future events. This drive, enhances performance and fosters resilience and determination in athletes. Near misses, therefore, play a crucial role in the pursuit of excellence in sports and competitions.
The Science Behind Near Misses
Understanding the science behind near misses helps us see why they’re so impactful on our emotions and behavior. Research into neuroscience and behavioral studies sheds light on this phenomenon.
Neuroscience Research
Neuroscience reveals that near misses trigger the brain’s reward system. Studies show that even without an actual reward, near misses activate the striatum, a key area involved in reward processing. Researchers found that dopamine—often associated with pleasure and motivation—spikes during near-miss events. This dopamine surge drives individuals to keep striving toward their goals despite setbacks.
Behavioral Studies
Behavioral studies provide insight into how near misses shape our actions. Experiments indicate that participants who experience near misses are more likely to persist in tasks compared to those who experience clear wins or losses. For instance, in gambling scenarios, near misses lead players to continue betting, believing they are close to winning. Similarly, in athletic contexts, near misses push athletes to train harder and enhance their performance. These findings highlight that near misses can foster a powerful drive to succeed, influencing both our motivation and behavior in profound ways.
Implications for Everyday Life
Understanding the power of near misses impacts various aspects of daily activities, influencing how individuals approach their goals and decisions.
Goal Pursuit
- Near misses affect how people pursue their objectives, providing a unique kind of motivation.
- When I nearly achieve something, it creates a powerful drive to keep going.
- People often feel a mix of arousal and frustration, which can boost resilience.
- If I miss a promotion by a small margin, I’ll likely work harder to secure it next time.
- Studies show that near misses activate the brain’s reward system, increasing dopamine levels and encouraging persistence (Clark, Lawrence, Astley-Jones, and Gray, 2009).
Decision Making
Near misses also shape decision-making processes. The heightened emotional response from almost succeeding makes people more inclined to take risks. When I experience a near miss, it alters how I weigh options, potentially leading to bolder choices. For instance, gamblers who narrowly miss a jackpot are more likely to keep playing, driven by the hope of winning in future attempts. The impact of near misses extends beyond gambling; it influences everyday decisions, encouraging a mindset geared toward achieving success despite potential setbacks.
Reference:
Clark, L., Lawrence, A. J., Astley-Jones, F., & Gray, N. (2009). Gambling Near-misses Enhance Motivation to Gamble and Recruit Win-related Brain Circuitry. Neuron, 61(3), 481-490.


 Taj Mackinolty – Author
Taj Mackinolty is a seasoned gambling enthusiast and writer at Smart Gamble Land. With a sharp focus on betting systems and winning strategies, Taj delivers clear and actionable content to readers looking to improve their gambling skills. His deep analytical approach and understanding of risk management allow him to break down complex techniques into simple guides. Taj is passionate about helping players gain control over their betting habits and develop a strategic mindset that can lead to long-term success in the casino environment.
Taj Mackinolty – Author
Taj Mackinolty is a seasoned gambling enthusiast and writer at Smart Gamble Land. With a sharp focus on betting systems and winning strategies, Taj delivers clear and actionable content to readers looking to improve their gambling skills. His deep analytical approach and understanding of risk management allow him to break down complex techniques into simple guides. Taj is passionate about helping players gain control over their betting habits and develop a strategic mindset that can lead to long-term success in the casino environment.
